Technical standards
EPIS tackles technical topics on an as-needed basis. Recently, EPIS has collaborated on
- Setting industry guidelines for RFID identification in the pulp supply chains
- Revision of EU ecolabel criteria for absorbent hygiene products, particularly related to fluff pulp
- Revision of ISO 4046 - vocabulary for the pulp and paper industry.
An example of technical standard collaboration was the creation of industry guidelines for radio-frequency identification (RFID) tracking for the pulp supply chains.

The market pulp producers want RFID to become the identification technology of choice in all parts of the global pulp supply chain.
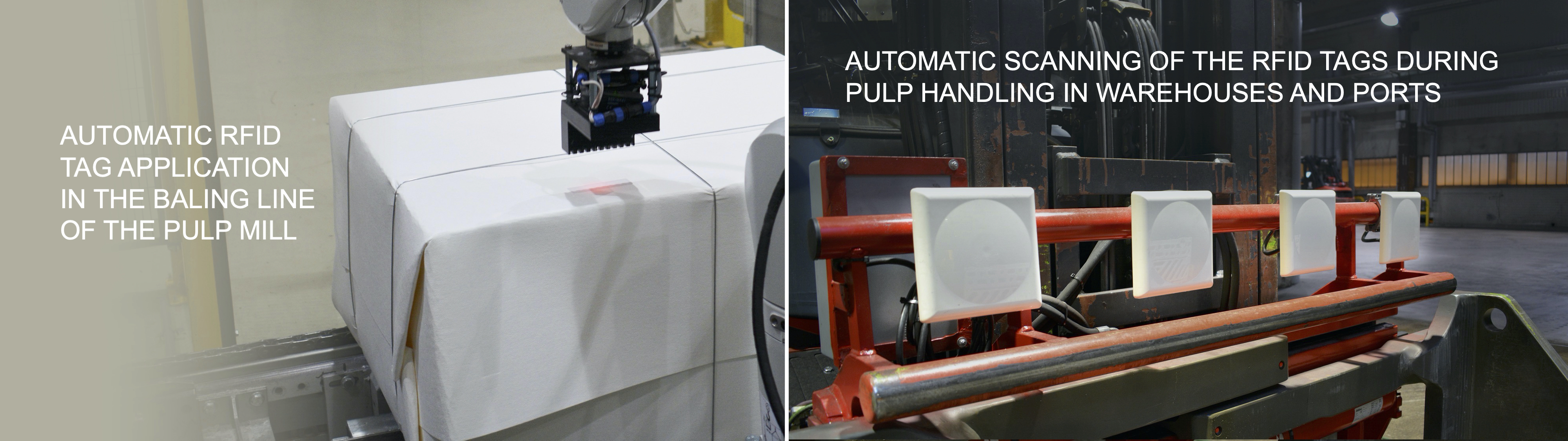
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) refers to a wireless system comprised of two components: tags and readers. The reader is a device that has one or more antennas that emit radio waves and receive signals back from the RFID tag. The tag is a light-weight repulpable label with a water-soluble adhesive and a lead-free metal alloy antenna conductor.
Key Process Steps
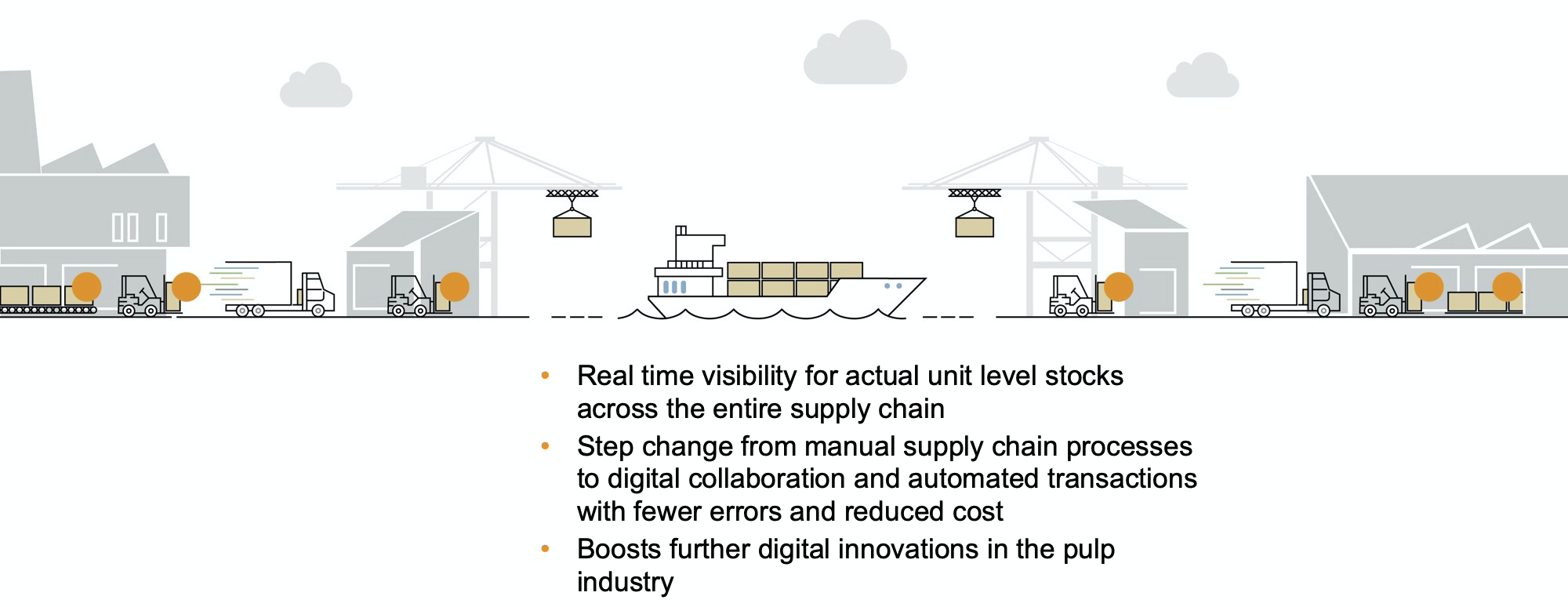
RFID is the enabler of digital collaboration between all parties of the supply chain
· RFID tags are applied to pulp units in pulp mills
· RFID tags are scanned during loading and discharging in all nodes of the supply chain
· Securing clean water
· RFID tags provide customers real-time inventory and quality data
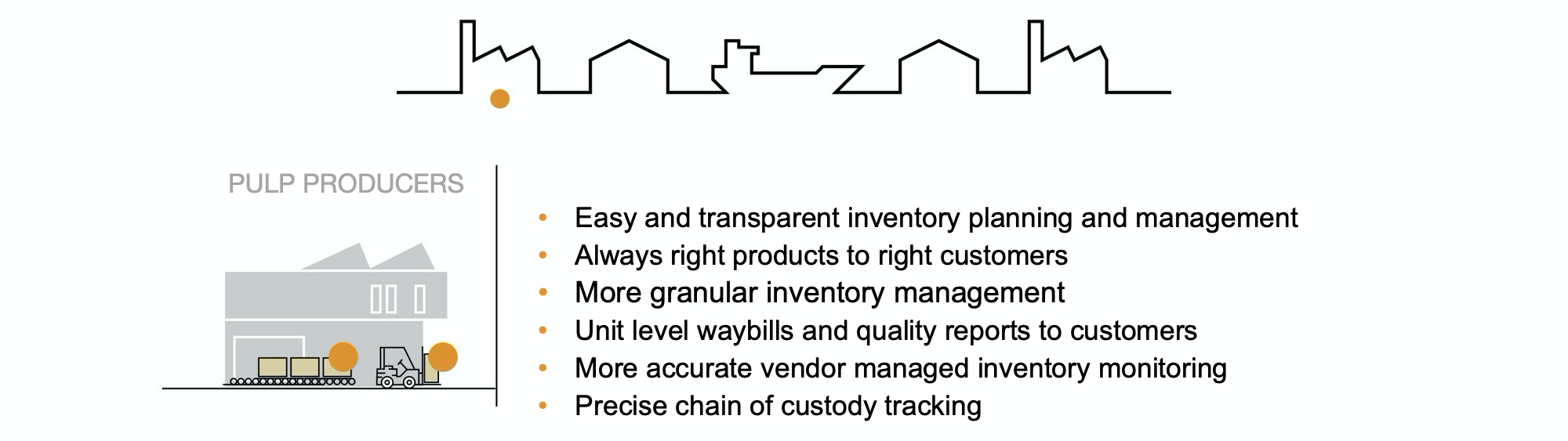
Benefits to producers
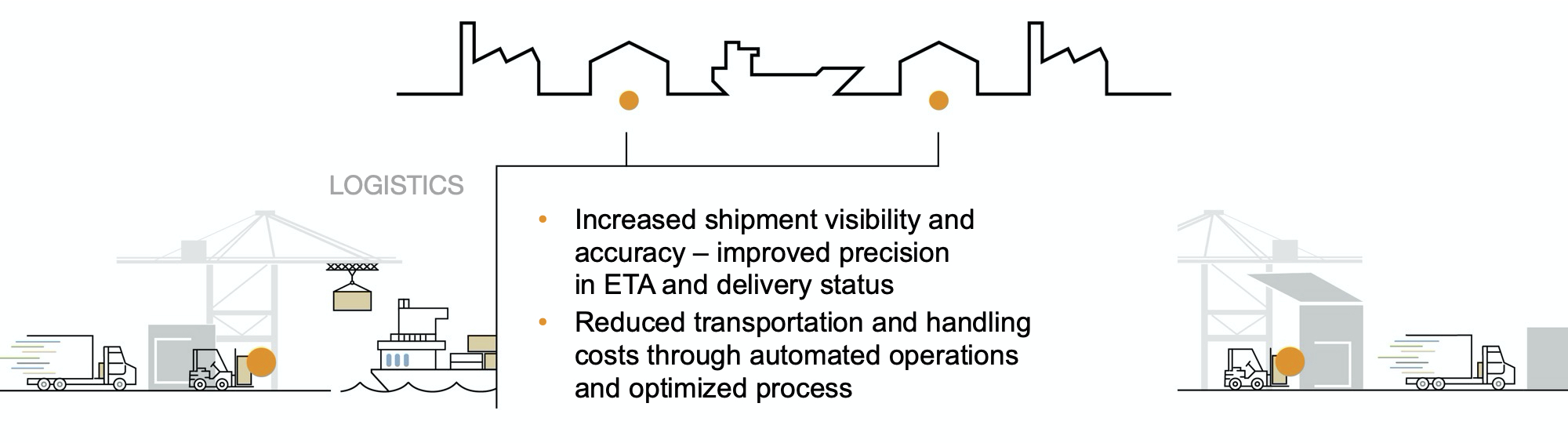
Benefits in logistics
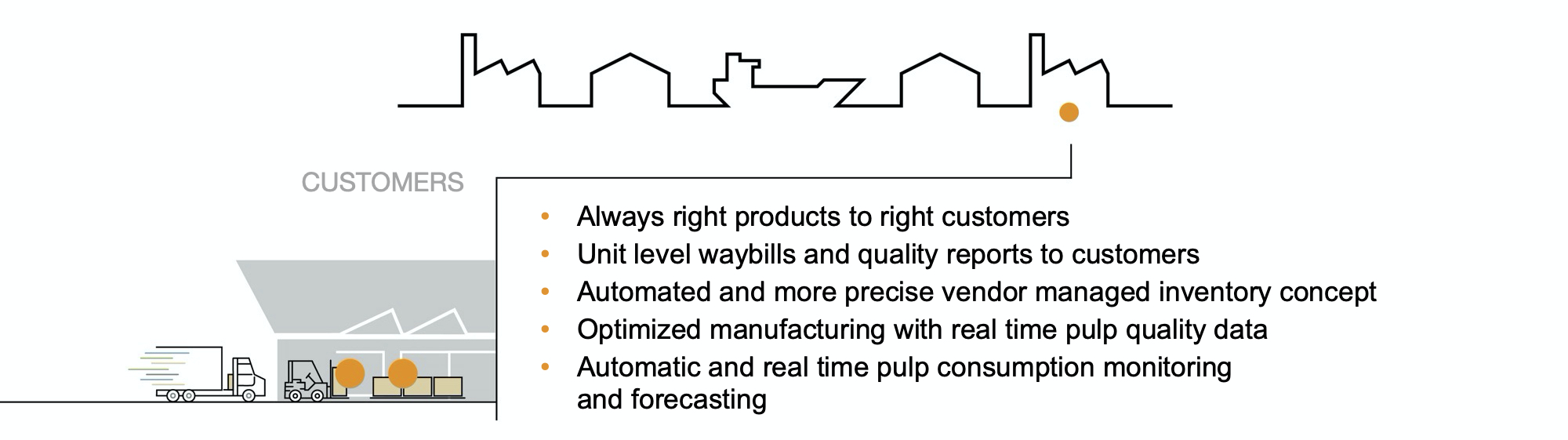
Benefits to customers
Benefits for the entire supply chain
Related links
GS1 RFID guidelines for pulp industry
Papinet message schemas for B2B integration in forest industry
Repulpability test: TAPPI UM-213, procedure A
